Chapter 24: Continuous RVs and PDFs
2023-11-08
Learning Objectives
Distinguish between discrete and continuous random variables.
Calculate probabilities for continuous random variables.
Calculate and graph a density (i.e., probability density function, PDF).
Calculate and graph a CDF (i.e., a cumulative distribution function)
Discrete vs. Continuous RVs
For a discrete RV, the set of possible values is either finite or can be put into a countably infinite list.
Continuous RVs take on values from continuous intervals, or unions of continuous intervals
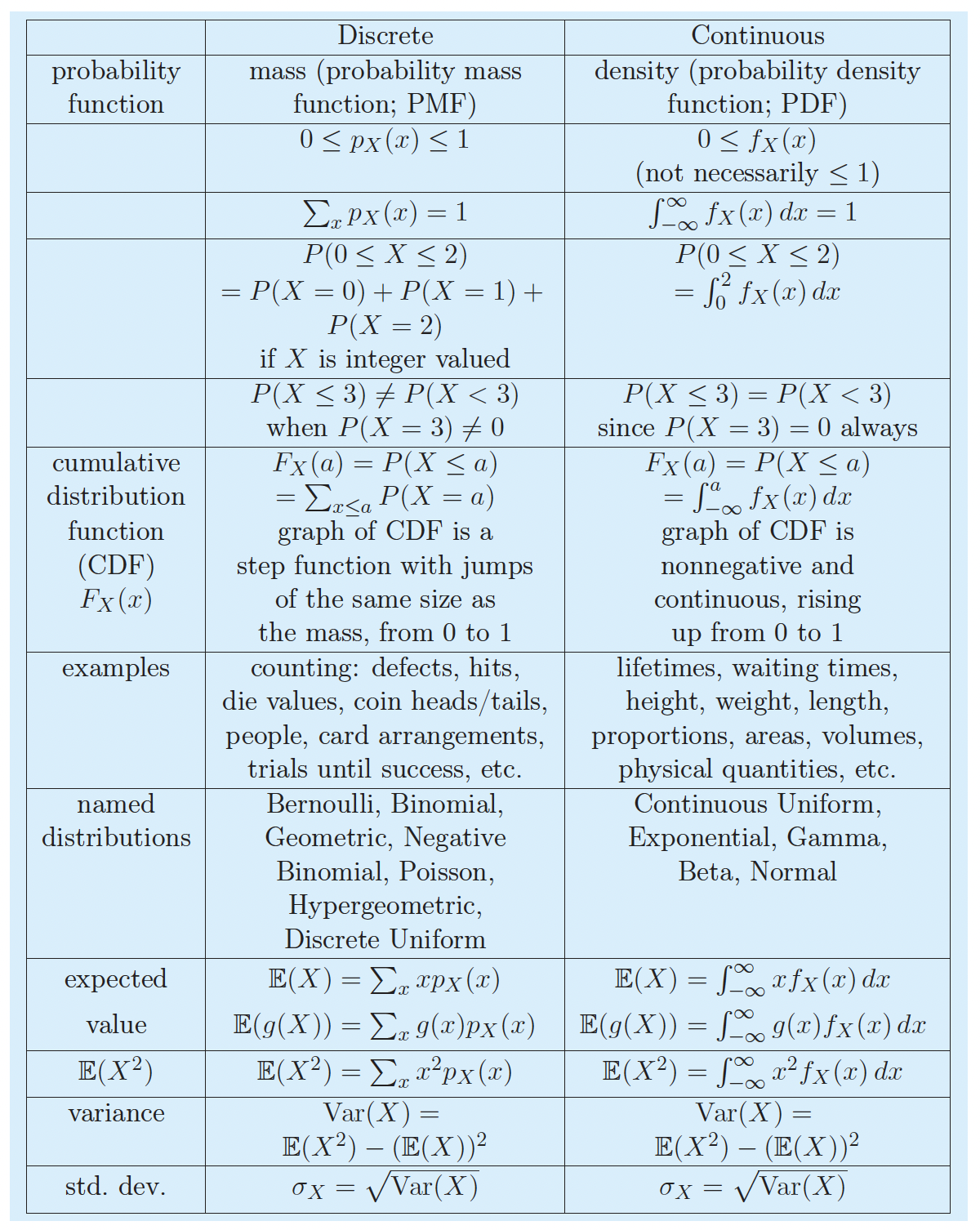
How to define probabilities for continuous RVs?
What is a probability density function?
Probability density function
The probability distribution, or probability density function (pdf), of a continuous random variable \(X\) is a function \(f_X(x)\), such that for all real values \(a,b\) with \(a \leq b\),
\[\mathbb{P}(a \leq X \leq b) = \int_a^b f_X(x)dx\]
Remarks:
Note that \(f_X(x) \neq \mathbb{P}(X=x)\)!!!
In order for \(f_X(x)\) to be a pdf, it needs to satisfy the properties
\(f_X(x) \geq 0\) for all \(x\)
\(\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f_X(x)dx=1\)
Let’s demonstrate the PDF with an example (1/5)
Example 1.1
Let \(f_X(x)= 2\), for \(a \leq x \leq 3\).
- Find the value of \(a\) so that \(f_X(x)\) is a pdf.
Let’s demonstrate the PDF with an example (2/5)
Example 1.2
Let \(f_X(x)= 2\), for \(a \leq x \leq 3\).
- Find \(\mathbb{P}(2.7 \leq X \leq 2.9)\).
Let’s demonstrate the PDF with an example (3/5)
Example 1.3
Let \(f_X(x)= 2\), for \(a \leq x \leq 3\).
- Find \(\mathbb{P}(2.7 < X \leq 2.9)\).
Let’s demonstrate the PDF with an example (4/5)
Example 1.4
Let \(f_X(x)= 2\), for \(a \leq x \leq 3\).
- Find \(\mathbb{P}(X = 2.9)\).
Let’s demonstrate the PDF with an example (5/5)
Example 1.5
Let \(f_X(x)= 2\), for \(a \leq x \leq 3\).
- Find \(\mathbb{P}(X \leq 2.8)\).
What is a cumulative distribution function?
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function (cdf) of a continuous random variable \(X\), is the function \(F_X(x)\), such that for all real values of \(x\), \[F_X(x)= \mathbb{P}(X \leq x) = \int_{-\infty}^x f_X(s)ds\]
Remarks: In general, \(F_X(x)\) is increasing and
\(\lim_{x\rightarrow -\infty} F_X(x)= 0\)
\(\lim_{x\rightarrow \infty} F_X(x)= 1\)
Let’s demonstrate the CDF with an example
Example 2
Let \(f_X(x)= 2\), for \(2.5 \leq x \leq 3\). Find \(F_X(x)\).
Derivatives of the CDF
Theorem 1
If \(X\) is a continuous random variable with pdf \(f_X(x)\) and cdf \(F_X(x)\), then for all real values of \(x\) at which \(F'_X(x)\) exists, \[\frac{d}{dx} F_X(x)= F'_X(x) = f_X(x)\]
Finding the PDF from a CDF
Example 3
Let \(X\) be a RV with cdf \[F_X(x)= \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 0 & \quad x < 2.5 \\ 2x-5 & \quad 2.5 \leq x \leq 3 \\ 1 & \quad x > 3 \end{array} \right.\] Find the pdf \(f_X(x)\).
Let’s go through another example (1/7)
Example 4
Let \(X\) be a RV with pdf \(f_X(x)= 2e^{-2x}\), for \(x>0\).
Show \(f_X(x)\) is a pdf.
Find \(\mathbb{P}(1 \leq X \leq 3)\).
Find \(F_X(x)\).
Given \(F_X(x)\), find \(f_X(x)\).
Find \(\mathbb{P}(X \geq 1 | X \leq 3)\).
Find the median of the distribution of \(X\).
Let’s go through another example (2/7)
Example 4.1
Let \(X\) be a RV with pdf \(f_X(x)= 2e^{-2x}\), for \(x>0\).
- Show \(f_X(x)\) is a pdf.
Let’s go through another example (3/7)
Do this problem at home for extra practice. The solution is available in Meike’s video!
Example 4.2
Let \(X\) be a RV with pdf \(f_X(x)= 2e^{-2x}\), for \(x>0\).
- Find \(\mathbb{P}(1 \leq X \leq 3)\).
Let’s go through another example (4/7)
Example 4.3
Let \(X\) be a RV with pdf \(f_X(x)= 2e^{-2x}\), for \(x>0\).
- Find \(F_X(x)\).
Let’s go through another example (5/7)
Do this problem at home for extra practice. The solution is available in Meike’s video!
Example 4.4
Let \(X\) be a RV with pdf \(f_X(x)= 2e^{-2x}\), for \(x>0\).
- Given \(F_X(x)\), find \(f_X(x)\).
Let’s go through another example (6/7)
Example 4.5
Let \(X\) be a RV with pdf \(f_X(x)= 2e^{-2x}\), for \(x>0\).
- Find \(\mathbb{P}(X \geq 1 | X \leq 3)\).
Let’s go through another example (7/7)
Example 4.6
Let \(X\) be a RV with pdf \(f_X(x)= 2e^{-2x}\), for \(x>0\).
- Find the median of the distribution of \(X\).
Chapter 24 Slides